A year ago I published a post on Protein and ageing, where I quickly explained the many roles of proteins in human physiology. Several reasons may lead individuals to increase their protein intake, depending on their specific health goals, lifestyles, and circumstances. Here are some common examples:
- Muscle building and strength training: People who engage in regular strength training or resistance exercises often require more protein to support muscle growth and repair. Athletes and bodybuilders may have higher protein needs.
- Ageing: As people age, there can be a natural decline in muscle mass and protein metabolism. Older adults may benefit from increased protein intake to maintain muscle mass, strength, and overall health.
- Weight management: Protein has a satiating effect and can help control appetite and reduce calorie intake. Including more protein in the diet can be beneficial for weight loss and weight management efforts.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Pregnant and lactating women require extra protein to support the growth and development of the fetus or infant. Protein is essential for the formation of tissues and organs in the baby.
- Wound healing and surgery: After surgery or injury, the body needs additional protein to repair damaged tissues and promote wound healing. Healthcare providers may recommend increased protein intake during recovery.
- Chronic Illnesses: Some medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, and certain gastrointestinal disorders, may increase protein requirements or alter protein metabolism. Healthcare professionals can provide guidance on individualised protein needs in such cases. Always consult your GP when you consider changing your diet and have a chronic condition.
- Vegetarian and vegan diets: Individuals following vegetarian or vegan diets may need to pay closer attention to protein intake to ensure they are getting enough essential amino acids. Plant-based protein sources can be lower in certain amino acids, so variety is key.
- Active lifestyles: People with physically demanding jobs or active lifestyles may need more protein to support their energy expenditure and overall health.
- Recovery from illness or infection: During illness or infection, the body’s protein needs can increase due to immune system activation and tissue repair. Adequate protein intake can help with a faster recovery.
- Malnutrition or undernutrition: Individuals who are malnourished or undernourished, whether due to poverty, food insecurity, or other factors, may need increased protein intake to address nutritional deficiencies.
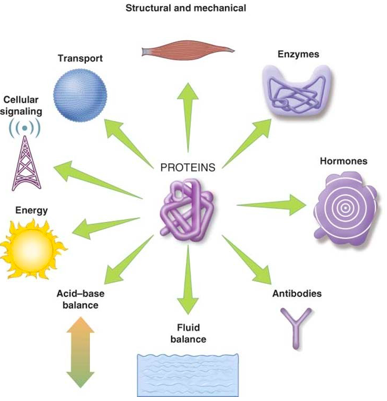
It’s important to remember that individual protein requirements can vary widely based on age, gender, activity level, health status, and other factors. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can help determine the appropriate protein intake for specific needs and goals, ensuring a balanced and healthy diet.